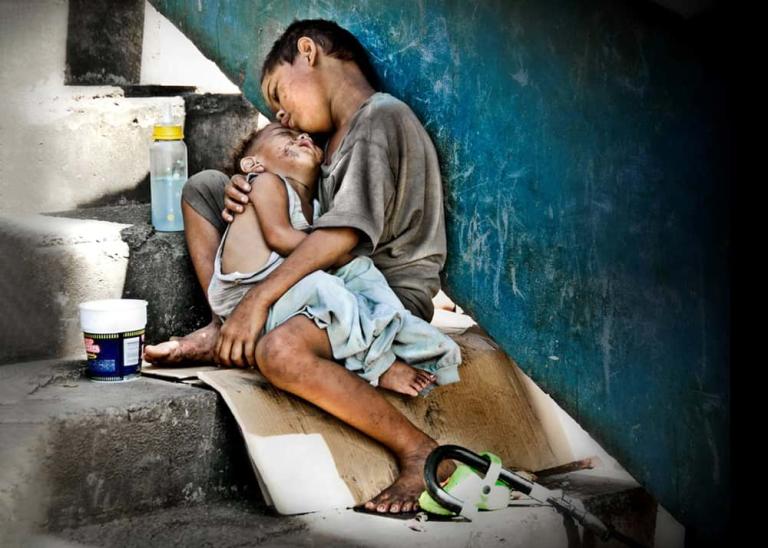
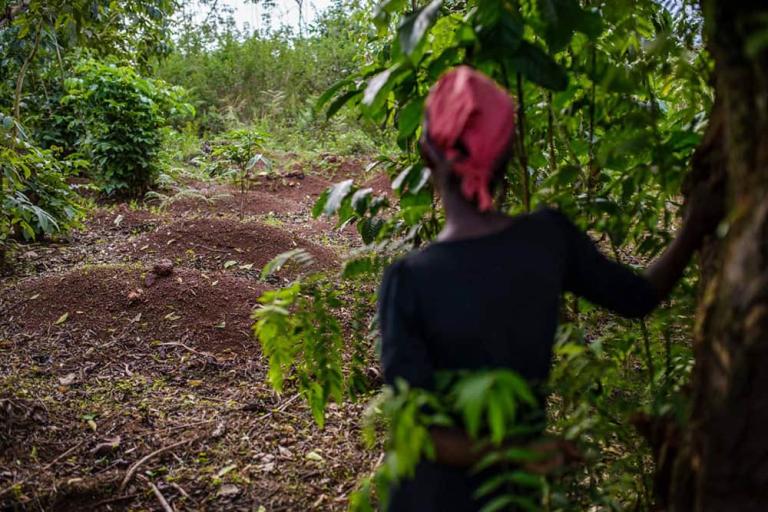
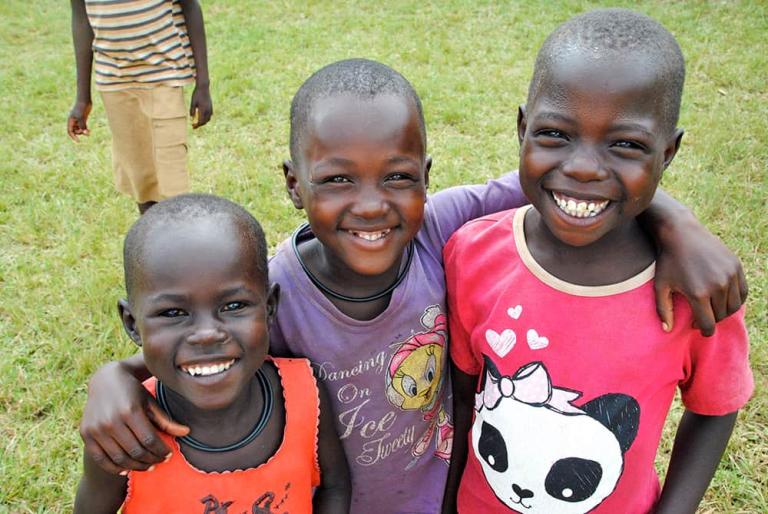
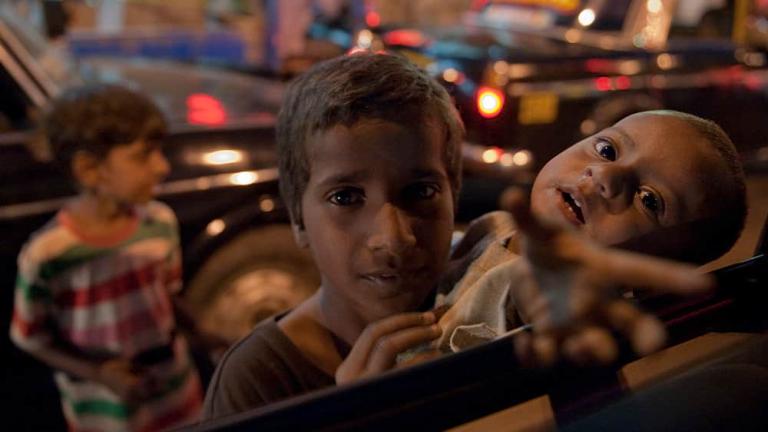
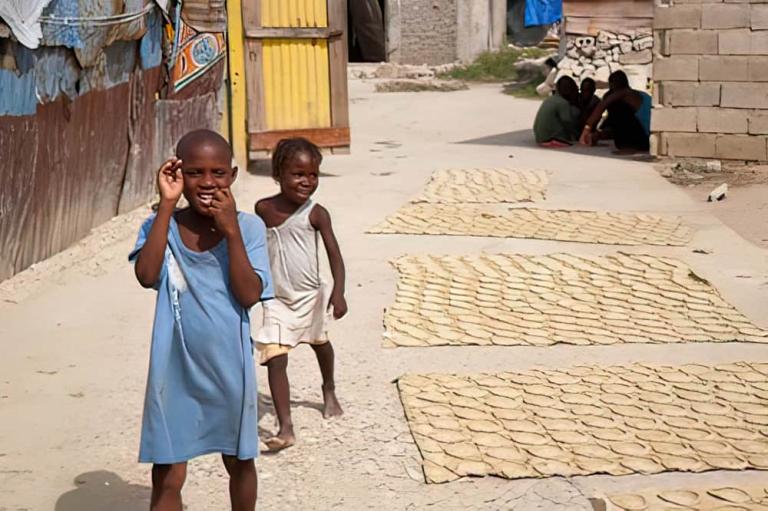
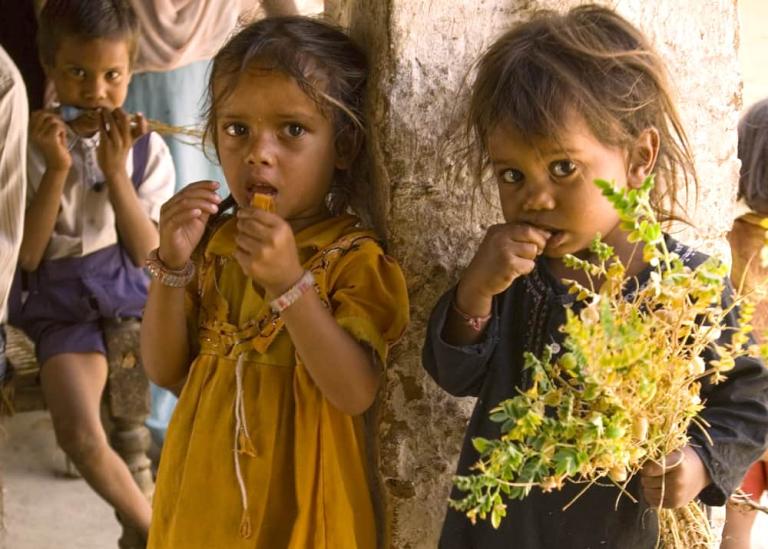
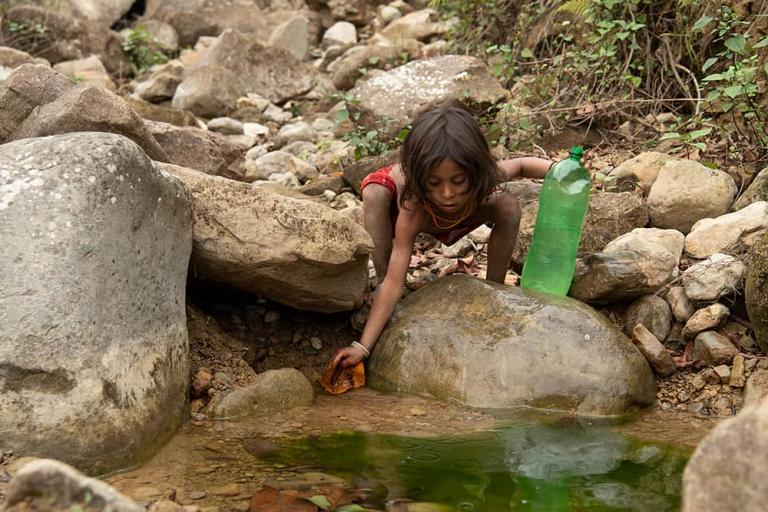
WILLS POINT, TX – Gospel for Asia (GFA World and affiliates like Gospel for Asia Canada) founded by KP Yohannan, issued a Special Report on the ugly truths of world hunger: “Scandal of Starvation” — world hunger is a long-term social and global crisis, directly or indirectly causing around 9 million deaths each year – more than AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis combined.

The War on Waste
Thankfully, efforts are being made to cut the terrible waste. The World Union of Wholesale Markets, a nonprofit group representing more than 150 wholesale markets around the world, has committed to new collaboration with the U.N.-FAO to improve distribution. Only a fraction of the food business world may be involved in the initiative, but it’s a start.
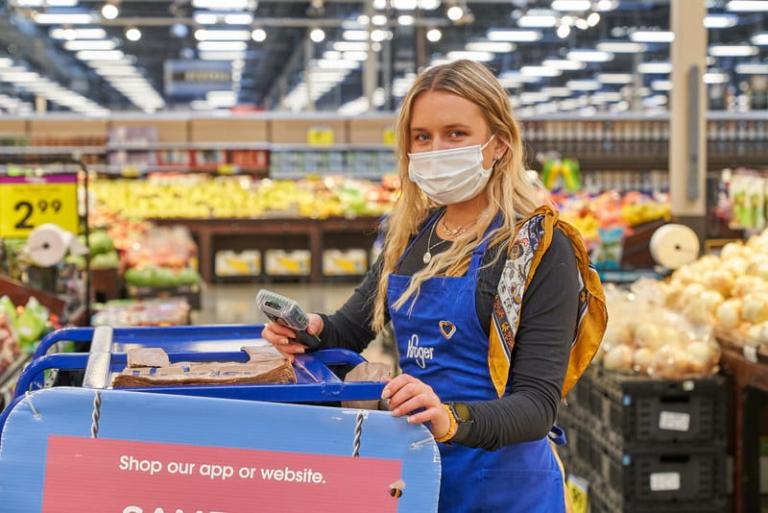

Meanwhile, big businesses are recognizing the need to be better stewards. At a special gathering on reducing loss hosted by the International Food Policy Institute, Kroger executive Denise Osterhues spoke of her company’s steps in that area. The senior director for corporate affairs told how Kroger had begun marking down red-bagged produce when it neared expiration date, introduced a “Pickuliar Picks” line of imperfect produce, and developed clearer date labeling to help consumers make the most of their food purchases.
Like a growing number of other food retailers and servers, Kroger also donates surplus and past-date supplies to charitable organizations for redistribution. It gave away 90 million pounds of produce in 2018.
Pope Francis, World Food Day 2019
Many different charitable organizations are eager to make use of produce that doesn’t get sold for one reason or another. In 2018, the 800 members of the Global FoodBanking Network alone distributed around half a million tons of food and grocery products.
At a plant in Sultana, in the heart of California’s breadbasket San Joaquin Valley, Gleanings for the Hungry recycles bruised and misshapen fruits and vegetables from growers in the area for shipping around the world. This ministry of Youth With a Mission (YWAM) takes its name from the directive in Leviticus 19 that the Israelites should not reap to the edges of their field, but leave the “gleanings” for the poor to gather up. For the last 40 years, Gleanings for the Hungry has processed and distributed millions of pounds of produce through partner organizations.
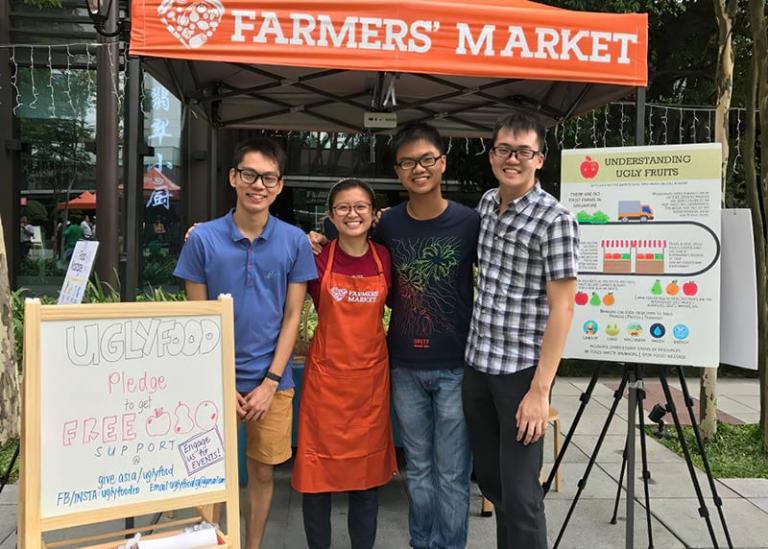

In Singapore, Pei Shan co-founded Ugly Food to make use of the produce that shoppers ignore because it doesn’t look nice enough. Her company turns the rejected items into healthy juices, ice cream bars, and fruit teas.
“Ultimately, we want our business to create a conversation about ‘cosmetic filtering’ and to help others rethink what they consider as waste,” she says.
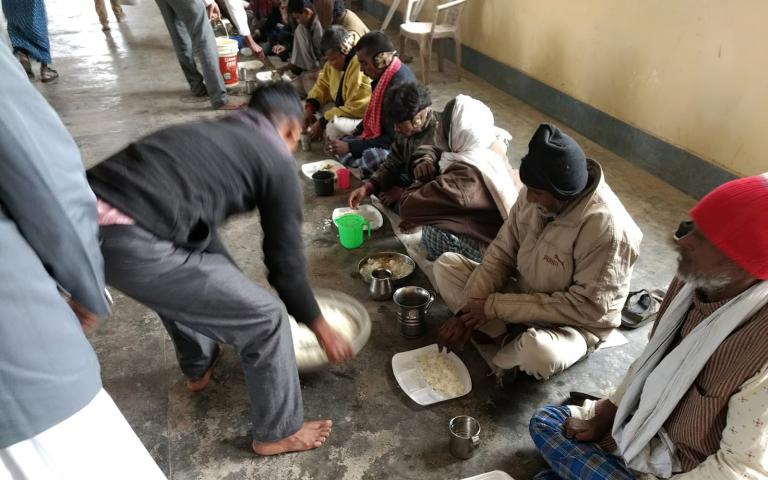
Feeding India’s Magic Wheels program is a fleet of trucks that collects unused food from canteens, wedding receptions, and other events for redistribution. The vehicles are equipped with temperature-controlled insulated boxes to keep the food fresh, and donors are given a liability release form to protect them. Feeding India has also set up Happy Fridges in residential and public spaces in 25 cities. The refrigerators are stocked free by donors, and available for anyone to come and take what they want, free of charge.
Launched in Delhi in 2014, the Robin Hood Army, a zero-funds organization that relies on volunteers to collect and distribute leftover food from restaurants and other businesses, has since served more than 26.5 million meals in more than 150 cities across a dozen countries.
How Hunger Harms the Human Body
Nutrition is about more than just having enough to eat, though. It’s having the right things to eat. Sometimes a body may be seemingly well-fed, but actually starving of the nutrients it really needs.
 That is why, though it seems almost contradictory, there has been an alarming rise in obesity, including in low-income countries in parts of sub-Saharan Africa and South and East Asia. A U.N. study in Latin America and the Caribbean found that the percentage of people there with obesity had tripled since 1975, while hunger increased 11 percent in the last four years.
That is why, though it seems almost contradictory, there has been an alarming rise in obesity, including in low-income countries in parts of sub-Saharan Africa and South and East Asia. A U.N. study in Latin America and the Caribbean found that the percentage of people there with obesity had tripled since 1975, while hunger increased 11 percent in the last four years.
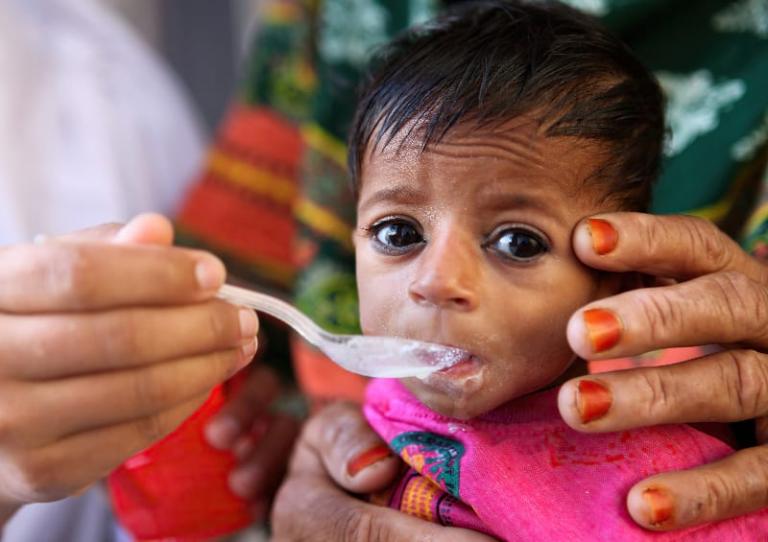
As a complex machine, the human body needs high-grade fuel to run well. Without it, systems start to break down. In parts of the world where food is scarce or of poor quality, the lack of vital vitamins and minerals has a serious impact.
Insufficient iron, a condition often made worse by malaria and other infectious diseases, makes pregnancy more risky and impairs physical and cognitive development. Lack of vitamin A can lower a person’s resistance to disease, impair growth in children and cause blindness. Lack of iodine is one of the major causes of reduced cognitive development in children.
All this lack of proper nutrition poses an especially severe threat to pregnant women and newborn babies: One in seven of 2015’s live deliveries—more than 20 million babies—had a problematically low birthweight.
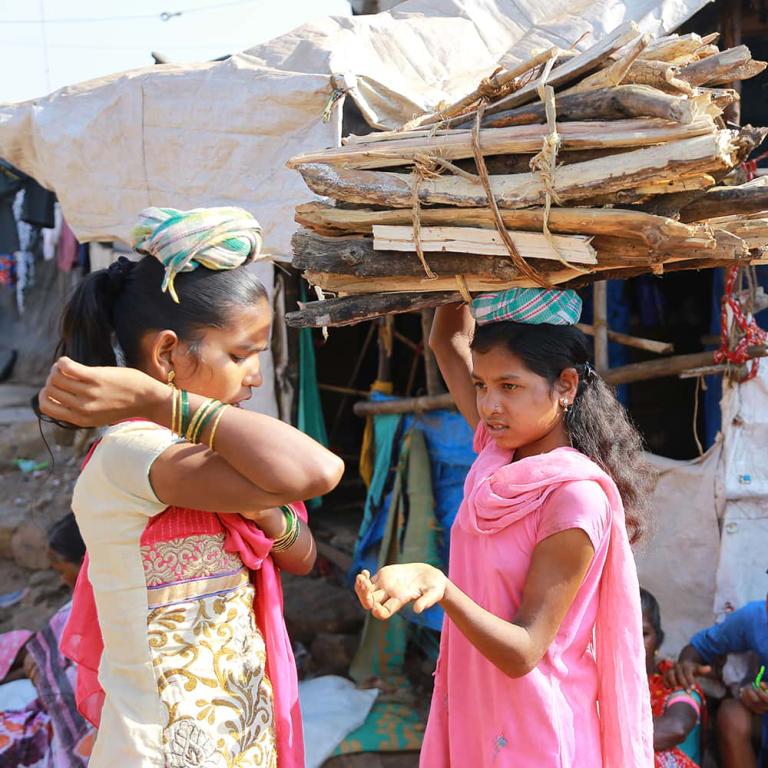
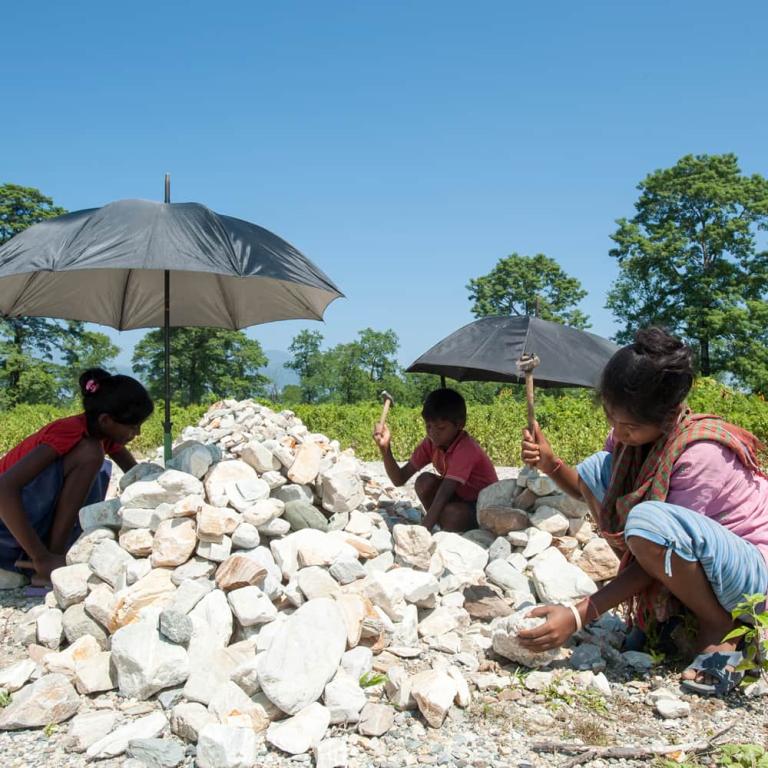
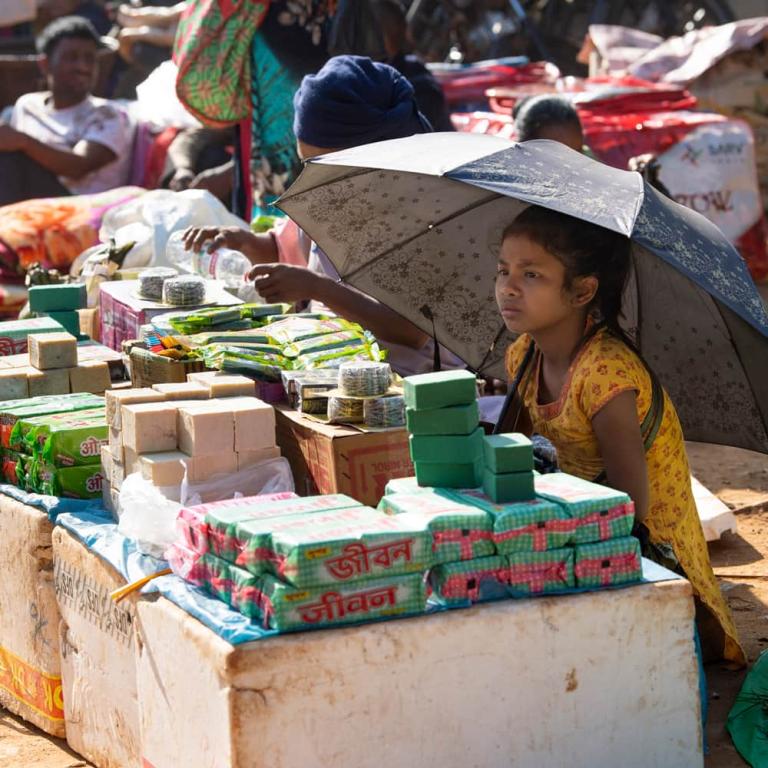
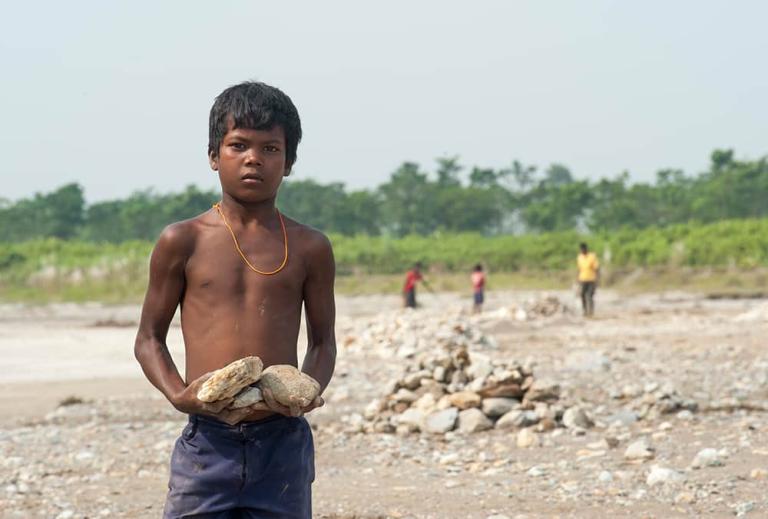
Hunger is inextricably linked to poverty, which in turn can’t be separated from war, political unrest,
and prejudice. Millions starve because of others’
actions and inactions, without even taking
into account natural disasters.
A good diet is especially crucial in the first three years, when young brains and bodies are developing. Ironically, malnutrition is linked to a higher risk of being overweight and chronic diseases like diabetes in later life.
An article by Lauren Weber graphically illustrated the importance of a good diet’s importance. A photograph featured in the article showed a dramatic difference between two five-year-olds born on the same day in Madagascar: Miranto, a good student, stood more than a head taller than Sitraka, who was unable to attend school because he hadn’t yet learned to speak properly and had trouble being still for any length of time. The difference? Their diet.
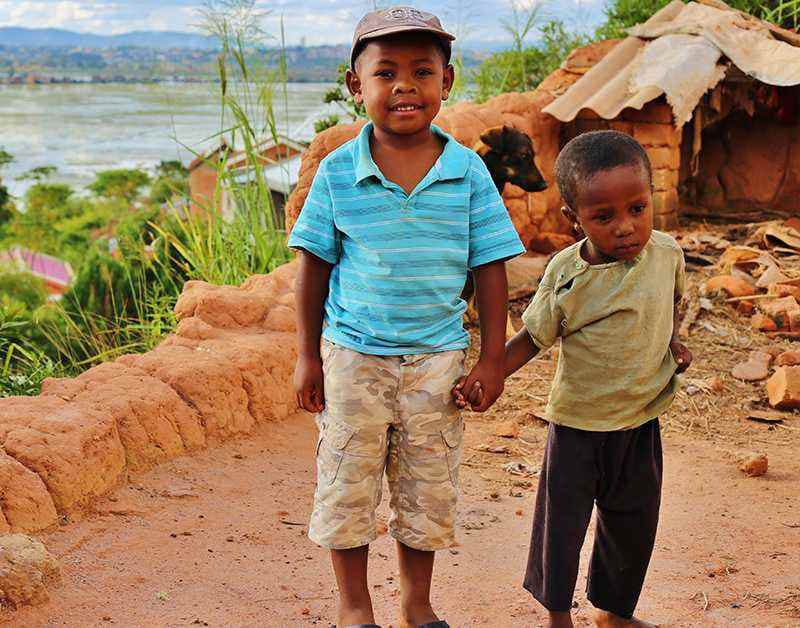

Sitraka was a victim of “stunting,” low height for age because of chronic nutrient deficiency. Like him, “most chronically malnourished children are shorter than their healthier peers,” she states.
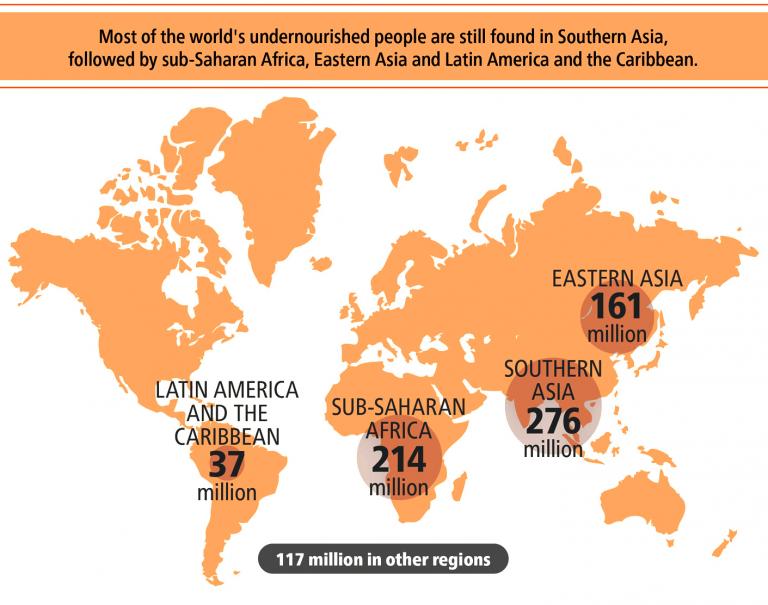
In 2017, the UN found almost 151 million children under age 5 were too short for their age due to malnutrition. Africa and Asia accounted for 39 percent and 55 percent of all stunted children, respectively. Nearly 38 percent of children under 5 in India were found to be stunted in 2018, accounting for a third of the world’s total. The countries with the next-highest numbers were Nigeria and Pakistan.
Such children’s immune systems are weaker, “leaving them more susceptible to repeated infections. And their brains do not develop fully, leading to lower IQs and a decrease in lifetime productivity” said Weber.
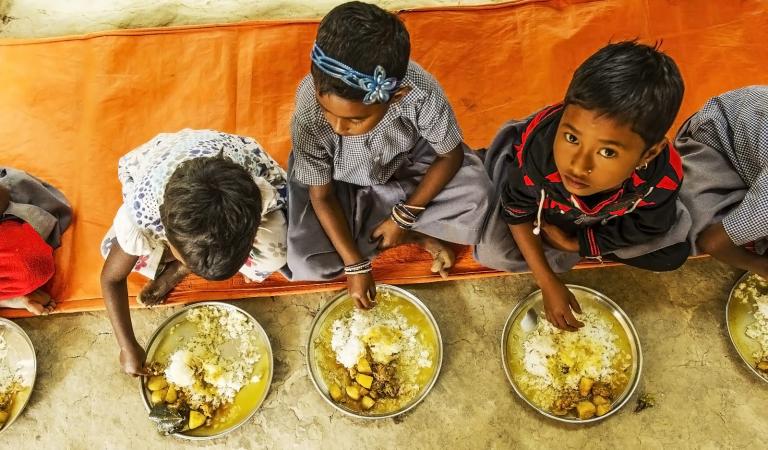
“Wasting,” meanwhile, is evidenced by low body weight for age, with the associated reduced muscle mass leaving children at greater risk of death from what might otherwise be minor infections. In 2017, one in ten children in Asia was underweight for their age, compared to just one in 100 in Latin America and the Caribbean.

Hunger’s Hidden Costs
The high cost of hunger might be seen better by evaluating its absence.
“In adulthood, per capita income of individuals who were not stunted at two years is higher compared to individuals who were stunted at two years,” said the U.N. “This increase comes about through the impact of improved nutrition on income through higher schooling and better cognitive skills. In fact, a reduction in global levels of stunting by 20 percent would represent a rise in income of 11 percent.”
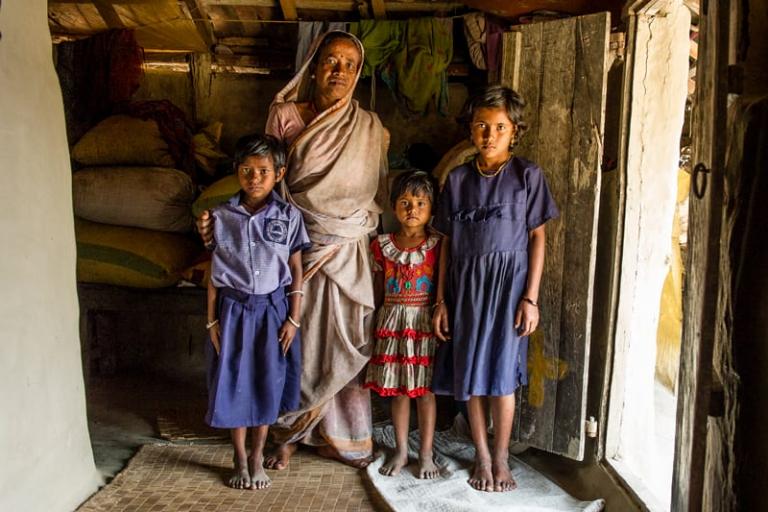

Hunger doesn’t just endanger people’s physical and intellectual development. It can damage their souls as well as their organs.
After visiting Zimbabwe, a country ravaged by drought and a sluggish economy, Hilal Elver, the UN Special Rapporteur on the Right to Food, noted some other effects of food scarcity.
“The most vulnerable segments of society, including the elderly, children and women, are forced to rely upon coping mechanisms such as, school dropout, early marriage, and sex trade to obtain food, behavioral patterns that often are accompanied by domestic violence,” she said. “This kind of struggle for subsistence affects their physical well-being and self-respect. It creates behavior and conditions that violate their most fundamental human rights.”
In common with other big social issues, it’s women and children who are often worst affected by hunger. Young women need iron-rich food to replenish what’s lost during menstruation, or they will face anemia, which can lead to heightened incidence of maternal deaths and stillbirths. A World Food Programme (WFP) study found 15- to 19-year-old girls in one part of Uganda had anemia rates two to three times higher than the national average.

The WFP report urged making greater efforts to keep adolescent girls in school and provide them with nutritious diets. A separate study by the organization found multiple benefits from school feeding programs in Indonesia. Enrollment, attendance, and understanding went up, while drop-out rates fell. The benefits went beyond the individual students and their futures, however.
Free school meals made limited household money available for other needs, which reduced the pressure on keeping kids away from school to help around the home or earn income. The study concluded that for every dollar invested in the feeding program there would be a five-fold return to the economy over the lifetime of each beneficiary.
As with all big social issues, hunger issues are complex. Hunger is inextricably linked to poverty, which in turn can’t be separated from war, political unrest, and prejudice. Millions starve because of others’ actions and inactions, without even taking into account natural disasters.
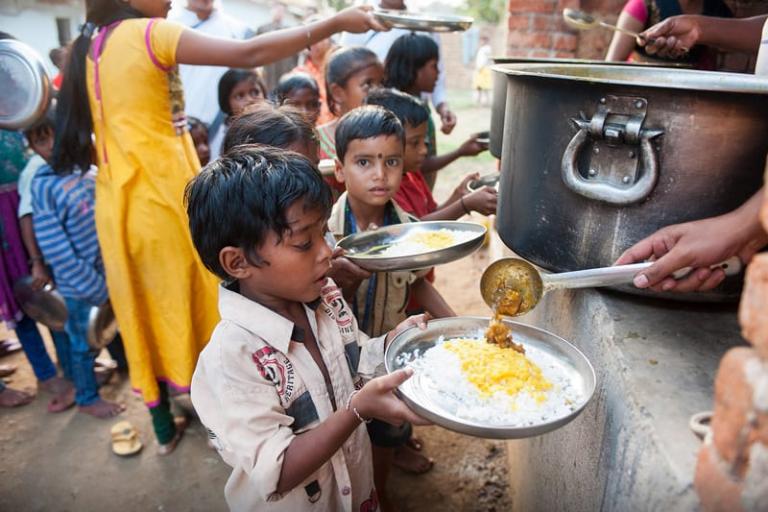

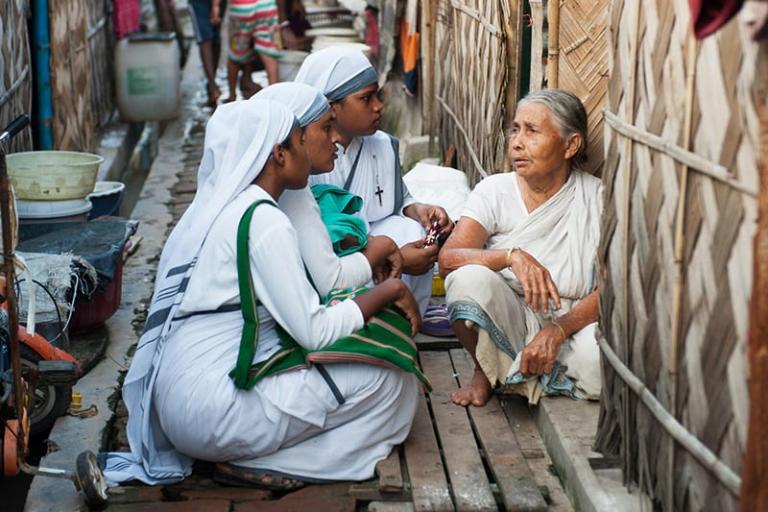
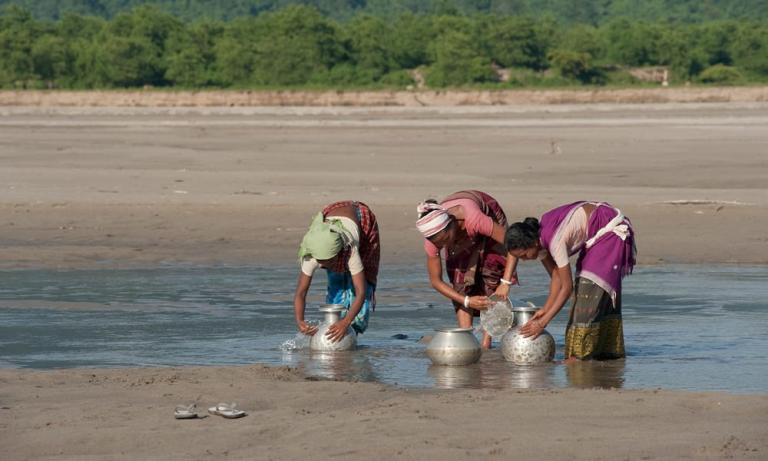
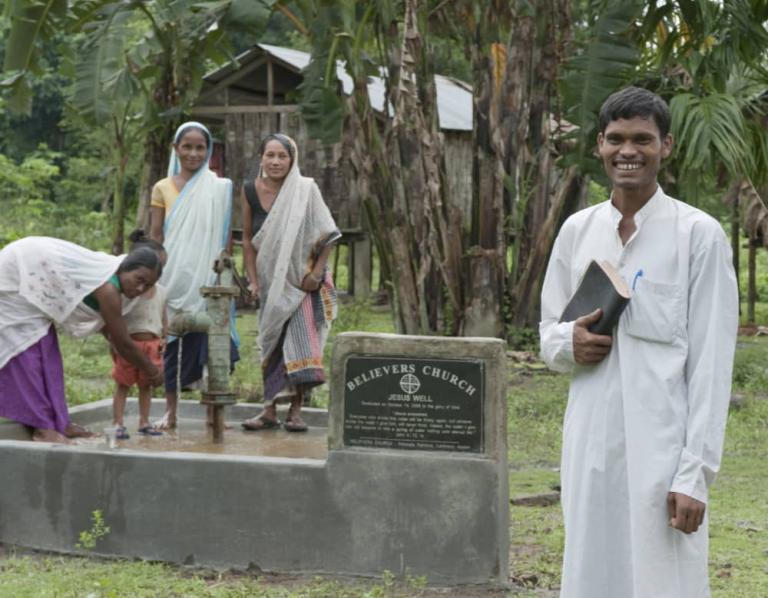
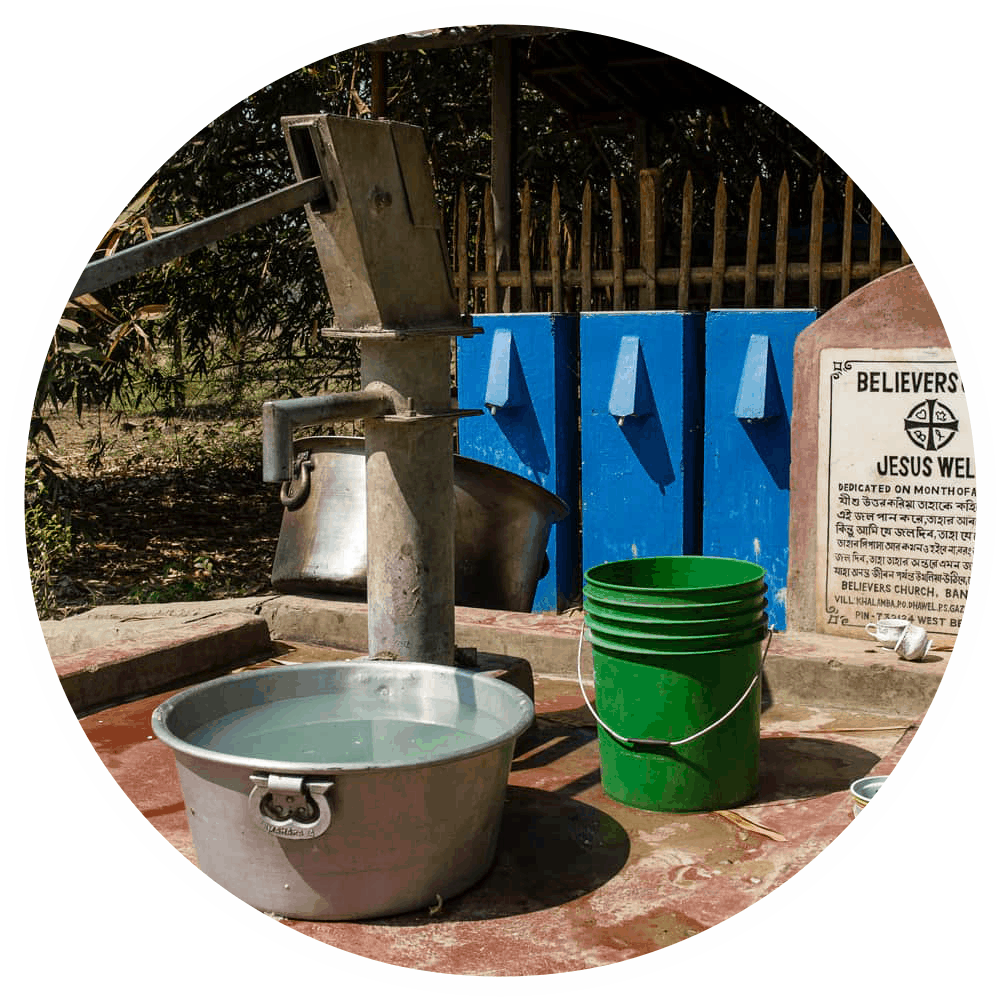
Malnutrition isn’t just a result of not having enough to eat, or even not having enough of the right things to eat. World Hunger notes that in many parts of Asia, “poor and insufficient sanitation and hygiene practices can increase the spread of disease and infection.” Two central sanitation issues contribute to up to half the cases of child malnourishment: the lack of access to clean water, and the presence of open defecation, which is still a problem in many parts of India. The elimination of the practice has been sought through a large-scale push of education and construction of community toilets undertaken by India’s government and non-profit groups such as Gospel for Asia (GFA).
In Ethiopia, a focus on ending open defecation helped to drastically improve nutrition levels and cut child stunting almost in half between 2000 and 2014, though the reduced 40 percent level remains “unacceptably high.”
The downward spiral of inadequate diet and poor sanitation and hygiene has been spotlighted in a United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund report: “Diarrhea or infectious disease can cause loss of micronutrients or inhibit consumption of sufficient nutritional foods, weakening an individual to become more susceptible to severe illness, and thus exacerbating the micronutrient deficiency.”
Give Food, Aid to Victims of Hunger & Starvation
Read the rest of Gospel for Asia’s Special Report on The Scandal of Starvation in a World of Plenty: World Hunger’s Ugly Truths Revealed — Part 1, Part 3
This Special Report originally appeared on gfa.org.
Read another Special Report from Gospel for Asia on Poverty: Public Enemy #1 – Eliminating Extreme Poverty Worldwide is Possible, But Not Inevitable.
Learn more by reading this special report from Gospel for Asia: Solutions to Poverty-Line Problems of the Poor & Impoverished — Education’s Impact on Extreme Poverty Eradication.
Click here, to read more blogs on Patheos from Gospel for Asia.
Learn more about Gospel for Asia: Facebook | YouTube | Instagram | LinkedIn | SourceWatch | Integrity | Lawsuit Update | 5 Distinctives | 6 Remarkable Facts | 10 Milestones | Media Room | Scandal of Starvation | Endorsements | 40th Anniversary | Lawsuit Response |
Notable News about Gospel for Asia: FoxNews, ChristianPost, NYPost, MissionsBox









































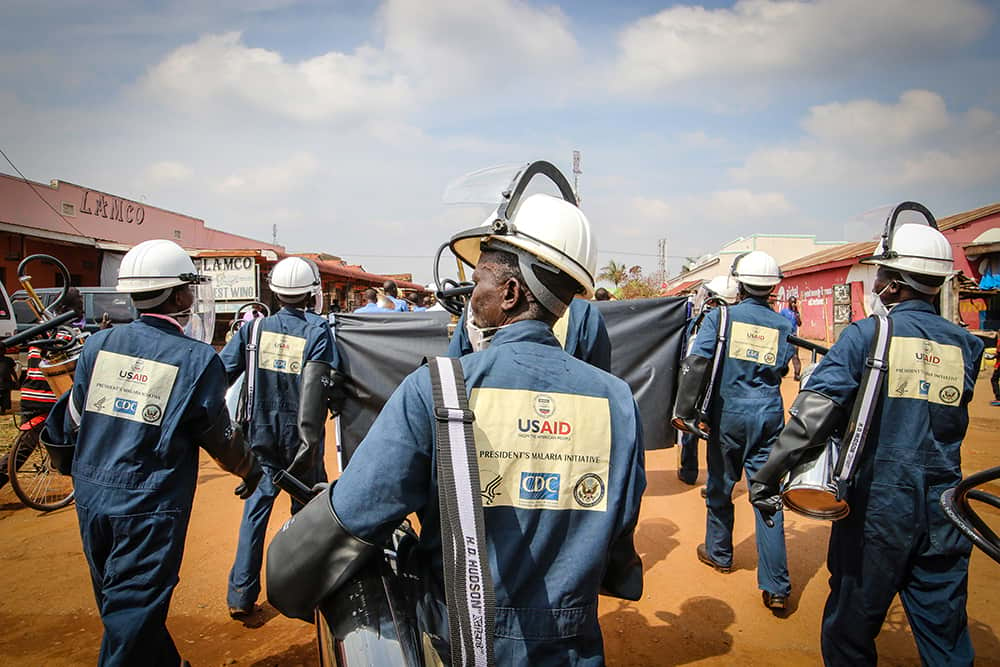
 In the seemingly never-ending quest to wipe out malaria—responsible in 2019 for the deaths of more than 400,000 people worldwide, roughly equivalent to wiping out the entire population of Miami, Florida—scientists are experimenting continually with new ideas to combat “the enemy” … the pesky mosquito.[
In the seemingly never-ending quest to wipe out malaria—responsible in 2019 for the deaths of more than 400,000 people worldwide, roughly equivalent to wiping out the entire population of Miami, Florida—scientists are experimenting continually with new ideas to combat “the enemy” … the pesky mosquito.[






















 “Many girls practice prostitution in our cities and even in our churches. Their parents encourage them because they are desperate for food, so they encourage their 15-year-old daughters to have sex to bring in money. It’s a desperation trade: ‘You help me, and I will have sex with you.’”
“Many girls practice prostitution in our cities and even in our churches. Their parents encourage them because they are desperate for food, so they encourage their 15-year-old daughters to have sex to bring in money. It’s a desperation trade: ‘You help me, and I will have sex with you.’”