Larry and Sergey soon began working on ways to harness information on the World Wide Web, spending so much time together that they took on a joint identity, "LarryandSergey." By 1996, Larry had hit on the idea of using the links between web pages to rank their relative importance. Borrowing from academia the concept of citations in research papers as a measure of topicality and value, he and Brin applied that thinking to the Web: if one page linked to another, it was in effect "citing" or casting a vote for that page. The more votes a page had, the more valuable it was. The concept seems rather obvious in retrospect, and today most search engines operate on this principle. But, at the time, it was groundbreaking. Calling their new invention Google -- a misspelling of a very large number in mathematics -- Larry and Sergey shopped it around to various companies for the price of $1 million.
No one was interested. In the technology boom of the late 1990s, conventional thinking was that so-called web portals like Yahoo! and AOL, which offered email, news, weather, and more, would make the most money. No one cared about search. But Sergey and Larry knew they were on to something, so they decided to take leaves of absence from Stanford and build a company themselves. Sergey's parents were skeptical. "We were definitely upset," Genia says. "We thought everybody in their right mind ought to get a Ph.D."
Soliciting funds from faculty members, family, and friends, Sergey and Larry scraped together enough to buy some servers and rent that famous garage in Menlo Park. Their venture quickly bore fruit: After viewing a quick demo, Sun Microsystems cofounder Andy Bechtolsheim (himself a Jewish immigrant from Germany) wrote a $100,000 check to "Google, Inc." The only problem was, "Google, Inc." did not yet exist -- the company hadn't yet been incorporated. For two weeks, as they handled the paperwork, the young men had nowhere to deposit the money.
 It is difficult to pinpoint the moment when Google became a true American phenomenon. Traditional measures, such as gracing the cover of Time magazine or being profiled on 60 Minutes, seem irrelevant when it comes to the fast-moving world of the internet. But there's no doubt about the date that Wall Street began to take the quirky California company seriously. It was April 29, 2004, when Google formally filed paperwork for its initial public offering of stock.
It is difficult to pinpoint the moment when Google became a true American phenomenon. Traditional measures, such as gracing the cover of Time magazine or being profiled on 60 Minutes, seem irrelevant when it comes to the fast-moving world of the internet. But there's no doubt about the date that Wall Street began to take the quirky California company seriously. It was April 29, 2004, when Google formally filed paperwork for its initial public offering of stock.
Two things shocked the investment world that day. First were the company's staggeringly large revenue and profit figures, which until then had been closely guarded secrets. No one had dreamed that the subtle text advertisements Google placed alongside search results -- which many web users don't even recognize as ads -- could be so profitable. Second was the ruthlessly earnest "founders' letter" that Sergey and Larry had included with the filing, which began by stating that Google was "not a conventional company" and did not intend to become one. They followed up that show of bravado by granting an interview to Playboy for publication during a mandatory "quiet period" before the public offering, when securities regulations restrict company executives' public comments. The misdeed prompted many to wonder whether the Google founders were careless and immature or just incorrigible troublemakers. It didn't help that they had decided to make it tough for Wall Street insiders to dominate the stock offering by selling shares via public auction -- their way of making the process more democratic and transparent.
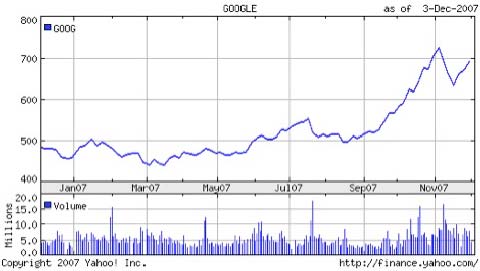
On August 16, 2004, its first day of trading, Google stock shot from $85 to $100 per share. Last November, it crossed the $500 mark, a number seldom seen in stock market history and far above the share prices of rivals Microsoft and Yahoo! At that price, Sergey and Larry, who together hold a controlling interest the company, each boast an estimated net worth of $15 billion.
What does that sort of money do to a 33-year-old? If you're Sergey, you buy a new house on the peninsula south of San Francisco, trade in your hybrid Toyota Prius for a fancier ride, and continue shopping at Costco. "From my parents, I certainly learned to be frugal and to be happy without very many things," Sergey tells me. "It's interesting -- I still find myself not wanting to leave anything on the plate uneaten. I still look at prices. I try to force myself to do this less, not to be so frugal. But I was raised being happy with not so much." His parents say Sergey taught them to shop at Costco, too. "He bought us a membership," Michael says. "It's a store that he knows and understands."
Sergey also understands something about cooking, a skill he picked up on his own. "A month before leaving [for Stanford], he realized he didn't know how to cook, so he learned," his mother tells me. Now, he owns a pasta machine and often joins his father in the kitchen when he comes home to visit. His specialty is Chernobyl Chili -- "45 minutes in the microwave."
The trappings of extreme wealth haven't passed Sergey by entirely. In 2005, he and Larry jointly purchased a Boeing 767 jet and had it refitted for personal use. Interior sketches of the "party airplane" -- which has two staterooms, sitting and dining areas, a large galley and seating for 50 -- surfaced in The Wall Street Journal last July. At one point, according to the plane's designer, the Google founders got into a spat over Sergey's insistence on a "California" king-sized bed in his private cabin. CEO Schmidt had to mediate, telling them, "Sergey, you can have whatever bed you want in your room; Larry, you can have whatever bed you want in your bedroom. Let's move on."
While everyone I've talked to who knows them well repeats the same line -- "They're good guys" -- gossip web sites occasionally print rumors of Larry and Sergey's soirees in posh private clubs and other typical jet-setter antics. They are without a doubt two of the most eligible bachelors on Google Earth, but both are reported to be in serious relationships: Larry with Stanford graduate student Lucy Southworth, and Sergey with Anne Wojcicki, a healthcare investor and the sister of Google executive Susan Wojcicki, who owned the garage where Google got started. In a 2001 interview for the now-defunct web site Women.com, Genia said she hoped Sergey would find "somebody exciting who could be really interesting to him . . . [who] had a sense of humor that could match his." As one might expect, she also prefers that Sergey marry a Jewish girl. "I hope that he would keep it in mind," she confided.
- Trending:
- Pope Leo Xiv
- |
- Israel
- |
- Trump
- |
- Social Justice
- |
- Peace
- |
- Love
The Story of Sergey Brin
May 20, 2010
Page: 5 of 7
more at patheos




