“Love your neighbor” includes God’s Creation. When we honor Creation, we show love for our neighbors with clean air, water, and land, and demonstrate our love for God who created us all.

Here are ideas for preaching and teaching Deuteronomy 6:1-9 and Mark 12:28-34 for Nov. 3, 2024. This is part of the EcoPreacher 1-2-3 series to equip preachers and congregations for engaging the Bible through an ecological lens. These texts are assigned as part of the Revised Common Lectionary for the twenty-fourth Sunday after Pentecost.
(If your church will be observing All Saints Day, see ideas for preaching here).
Eco-Exegesis
Eco-exegesis is a method of interpreting the biblical text through a green lens using the principles of ecological theology.
Deut. 6:3
Hear therefore, O Israel, and observe [the commandments] diligently, so that it may go well with you, and so that you may multiply greatly in a land flowing with milk and honey, as the Lord, the God of your ancestors, has promised you.
In Deuteronomy Chapter 6, Moses is addressing the Israelites and reminding them of their covenant with God as they prepare to enter the Promised Land. Notice the connection between God’s commandments, the people, and the land in this passage.
The Israelites are charged with adhering to ethical behavior toward each other not just for themselves, but for the sake of the generations who follow and for the land itself.
Biblical and ecological ethics
In Eco Bible, Rabbis Yonatan Neril and Leo Deo explain that while the Torah obviously does not address contemporary ecological concerns such as climate change, ocean acidification, or microplastics, the ethics of doing what is right in the eyes of God “requires that we bring religion to bear on the current specific issues and over ecological crises” (Eco Bible Vol. 2, 140).
Simply put, the land cannot provide the means by which we enjoy “milk and honey” if the ecosystem is poisoned, and if the habitat for bees is destroyed and pesticides are used that kill off their colonies.
Teach them to your children

Moses is clear in this passage that loving God entails being in right relationship with each other and with the Earth that God has entrusted to us. Loving your neighbor also requires teaching children to cherish and protect habitats, plants and animals, waterways, and the air we breathe.
As Richard Louv asserts in his book, Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children from Nature-Deficit Disorder, children will not save what they do not love. When we foster children’s love and appreciation of nature, they will be inspired to support or even take part in conservation efforts as adults.
Talk about God’s ethics for Earth
Cultivating a faith-centered environmental ethic also necessitates being in conversation with other people within our house of worship.
In a grant project that I’m directing with The BTS Center and Creation Justice Ministries, we surveyed nearly 200 parishioners in thirty congregations from various denominations across the U.S. Even though 93% said they were very or somewhat concerned about the climate crisis, they estimated that only about 75% of their fellow parishioners shared their concern. Also, less than half of them (45%) said they heard climate or environmental issues being discussed in their church on a regular basis.
It follows, then, that more discussion about these issues is needed in congregations. We must “talk about them when we are at home and when we are away, when we lie down and when we rise” (Deut. 6:7).
Mark 12:29-31
Jesus answered, “The first is, ‘Hear, O Israel: the Lord our God, the Lord is one; 30you shall love the Lord your God with all your heart, and with all your soul, and with all your mind, and with all your strength.’ 31The second is this, ‘You shall love your neighbor as yourself.’ There is no other commandment greater than these.”
In this passage in the Gospel of Mark, a scribe comes upon Jesus and the religious leaders engaged in a heated argument. They tried to trap Jesus (12:13-17) and engage him in nonsensical disputes (12:18-27).
So the scribe cuts to the chase with a question about the greatest commandment. Jesus directly quotes Deut. 6:4 as well as Leviticus 19:18: love God and love your neighbor. The scribe affirms Jesus’s answer and adds that following those commandments are “much more important than all whole burnt offerings and sacrifices” (12:33). In response, Jesus says that the man is “not far from the kingdom of God” (12:34).
Why did Jesus consider the scribe’s answer to be wise? And what does this imply for an ecological ethic?
One of the primary purposes of burnt offerings and sacrifices was to atone for sin. But if one’s intention is to be in right relationship with God and neighbor from the start, there would be little need for offerings and sacrifices. As the saying goes, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
This is why the scribe says that following the commands to love God and love your neighbor is “more important” than the performing the sacrifices for breaking those commands.
There is a natural application of this passage to contemporary environmental issues.
If our decisions about how we produce energy, food, homes, and transportation were guided by an ethic of being in right relationship with God and neighbor from the start, there would be much less need to clean up the mess of our ecological sins afterward.
For example, the effort put into mitigating climate change is much less than the cost and effort to recover from climate-fueled weather events. And the effort expended for ensuring clean water, land, and air is much less than the effort of dealing with the public health costs and the suffering of countless people.
Thus, loving your neighbor and loving God requires loving Creation.
1 Eco-Idea
The Eco-Idea is one succinct statement that tells us who God is and/or what God does in relation to Creation and how we should respond as people of faith.
When we honor Creation, we honor our neighbors with clean air, water, and land, and demonstrate our love for God who created us all.
2 Eco-Questions
Eco-Questions are what we can ask to help a congregation draw out the implications of the Eco-Exegesis and Eco-Idea.
- In what ways does your congregation demonstrate love for both God and neighbor through care of Creation? What ministries of environmental advocacy and action help you love your neighbor?
- If “milk and honey” are symbols of health and flourishing, how can your congregation support organic farms and apiaries to ensure the health of pastures and bee colonies?
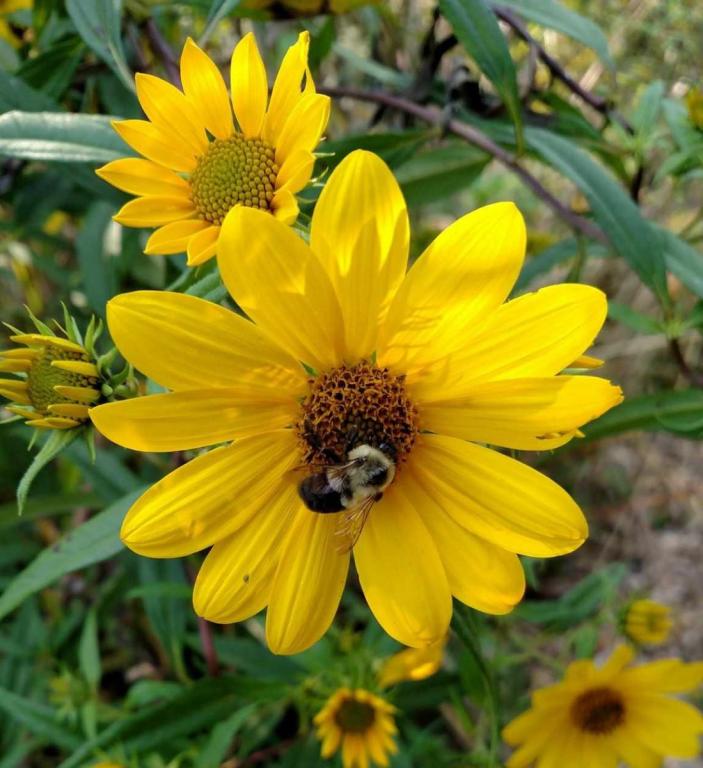

3 Eco-Actions
Eco-Actions are ways that a congregation might respond to the Eco-Idea and Eco-Questions. One of these possibilities may have salience for your ministry context.
1 – Invite
Invite a local beekeeper to a forum to talk about how they work for the health and sustainability of bee colonies as well as protect bees from disease and environmental threats. Also, organize a field trip to a local organic farm where cows are allowed to roam in green pastures instead of being locked in stalls. Ask the farmer to explain the challenges and benefits of organic farming.
2 – Learn
Learn what the Environmental Protection Agency is doing to protect pollinators here: https://www.epa.gov/pollinator-protection/epa-actions-protect-pollinators. Also, click here to learn what you and your church can do to protect honey bees and other pollinators.
3 – Vote
Vote for elected officials who demonstrate a commitment to caring for both people and planet. Learn about the environmental policies of the presidential candidates here.
Read also:
Grieving Extinct Species on All Saints Day
Bringing Our Faith to the Ballot Box: All Saints Sunday Sermon
EcoPreacher 1-2-3 is a partnership between the Rev. Dr. Leah Schade and the Interfaith Center for Sustainable Development, publishers of Eco Bible, a Jewish ecological commentary on the Hebrew Scriptures. EcoPreacher 1-2-3 provides Creation-centered sermon preparation that is short, accessible, and based on a solid biblical foundation. To see other EcoPreacher ideas and to sign up to receive future EcoPreacher 1-2-3 installments, click here.

The Rev. Dr. Leah D. Schade is the Associate Professor of Preaching and Worship at Lexington Theological Seminary in Kentucky and ordained in the ELCA. Dr. Schade does not speak for LTS or the ELCA; her opinions are her own. She is the author of Preaching and Social Issues: Tools and Tactics for Empowering Your Prophetic Voice (Rowman & Littlefield, 2024), Preaching in the Purple Zone: Ministry in the Red-Blue Divide (Rowman & Littlefield, 2019) and Creation-Crisis Preaching: Ecology, Theology, and the Pulpit (Chalice Press, 2015). She is the co-editor of Rooted and Rising: Voices of Courage in a Time of Climate Crisis (Rowman & Littlefield, 2019). Her book, Introduction to Preaching: Scripture, Theology, and Sermon Preparation, was co-authored with Jerry L. Sumney and Emily Askew (Rowman & Littlefield, 2023).