WILLS POINT, TX – GFA World (Gospel for Asia) founded by K.P. Yohannan, has been the model for numerous charities like GFA World Canada, to help the poor and deprived worldwide, issued this first part of a Special Report on Malaria – new vaccine heralds a game-changing development.
It’s the “buzz” millions around the world have been waiting to hear—the news of a mosquito-busting breakthrough decades in the making.
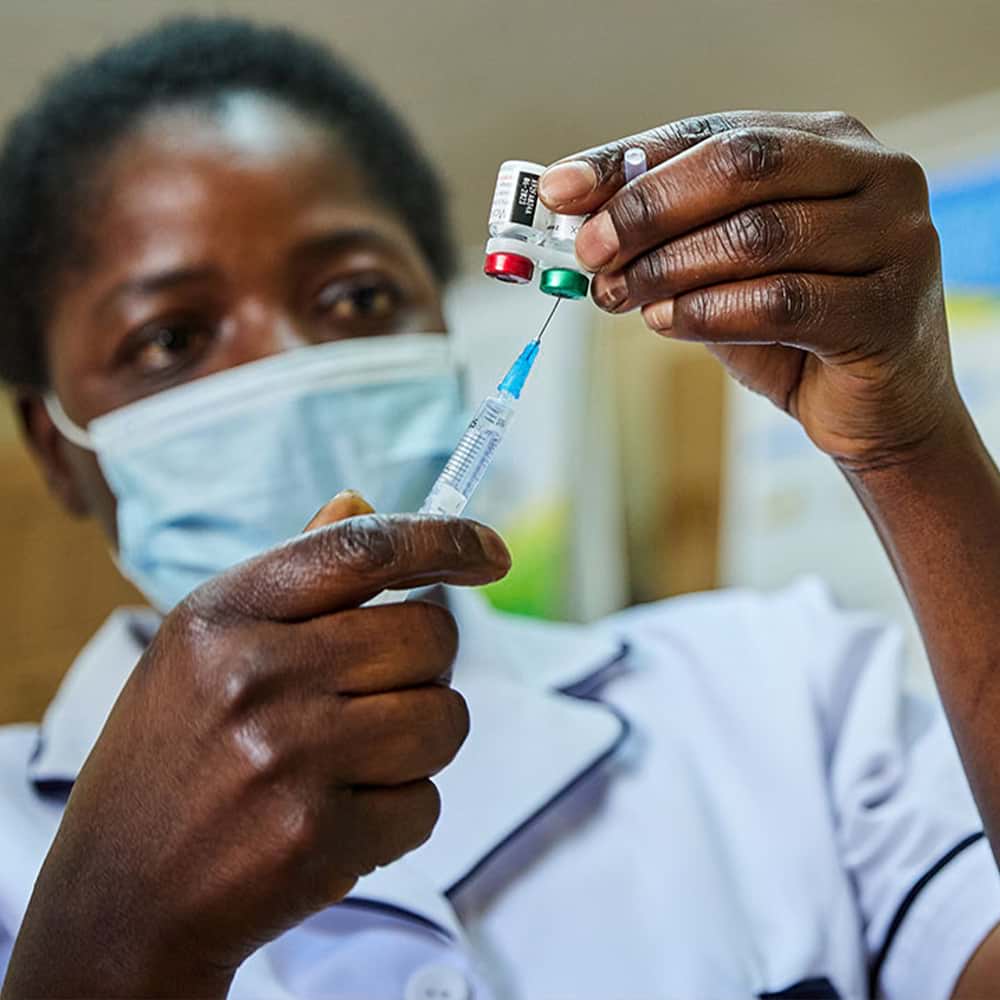
On Oct. 6, 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that for the first time ever it was recommending the widespread use of a vaccine to protect children at risk of mosquito-borne malaria—one of the biggest killers of children under 5 in sub-Saharan Africa.[1]
In a news universe saturated by COVID-19 recently, this “historic” announcement struggled to make a splash in the mainstream media. But in the ongoing worldwide battle against life-threatening mosquito bites, this vaccine heralds a game-changing development in the fight against malaria.
“This is a historic moment,” said WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus. “Using this vaccine on top of existing tools to prevent malaria could save tens of thousands of young lives each year.”[2] Every year, more than 260,000 children under the age of 5 in sub-Saharan Africa die from the effects of malaria, according to WHO.[3]
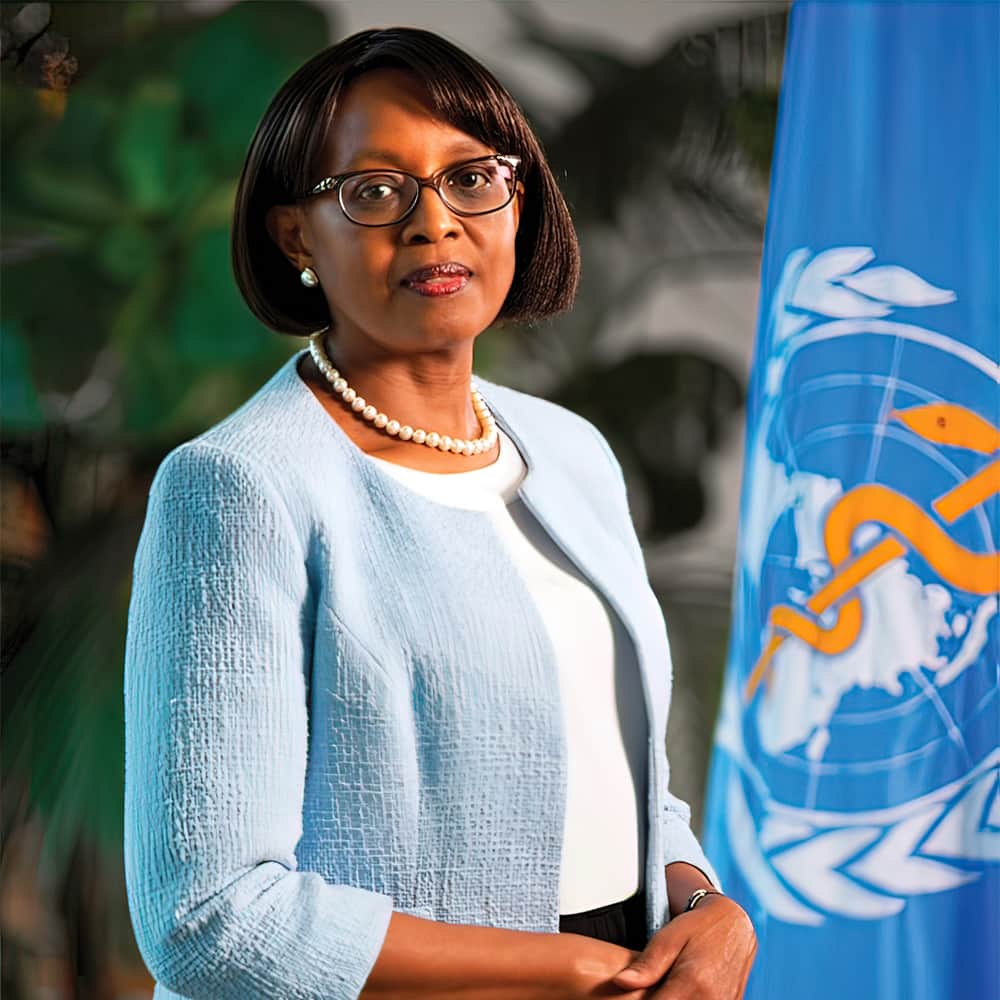

After years of stagnated progress in the fight against the disease in nations such as Ghana, Kenya and Malawi, the breakthrough finally came with a trial vaccine known as RTS, S/AS01—not exactly a memorable name for such a landmark moment.
WHO endorsed widespread use of the four-dose vaccine in areas with “moderate to high P. falciparum malaria transmission,” following a pilot program that’s involved giving the shot to more than 900,000 children since 2019.[4] P. falciparum is also the most prevalent strain in Africa.
“For centuries, malaria has stalked sub-Saharan Africa, causing immense personal suffering,” said Dr. Matshidiso Moeti, WHO’s Africa Regional Director. “We have long hoped for an effective malaria vaccine, and now for the first time ever, we have such a vaccine.”[5]
The breakthrough offers “a glimmer of hope” for the continent that “shoulders the heaviest burden of the disease,” Moeti said.[6]
As of October 2021, more than 2.3 million shots-in-arms had been administered to children in the three-nation pilot program, covering parts of Ghana, Kenya and Malawi. Initial results indicated that more than two-thirds of children who were not sleeping under insecticide-treated bed nets were protected by the vaccine. And the shot—more than 30 years in the making—reduced cases of severe and deadly malaria by 30 percent.[7]
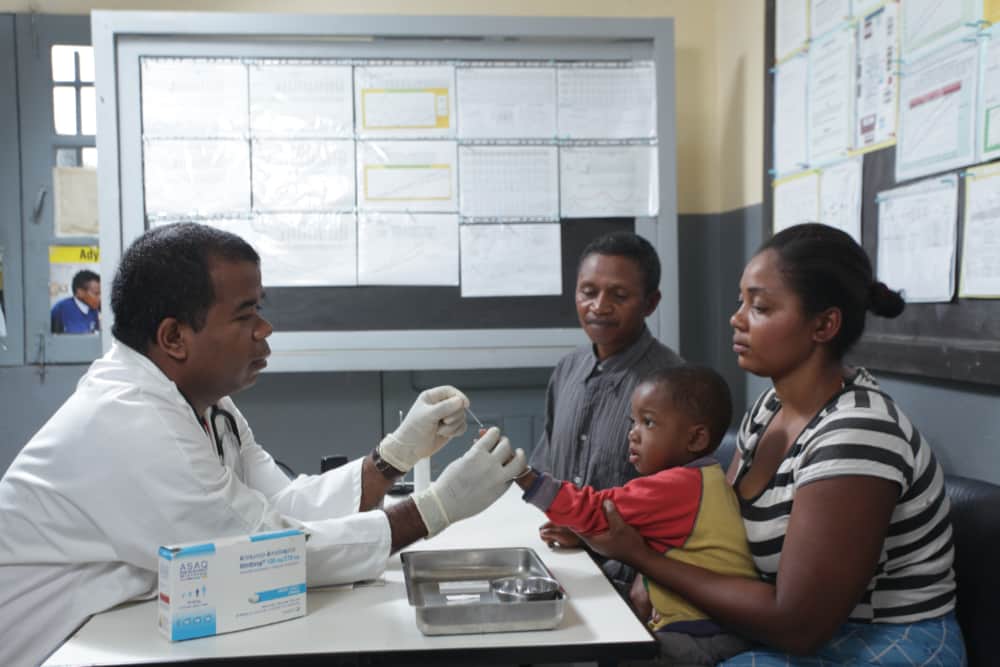
Malaria and Changing Temperatures
The encouraging news, at long last, of an effective vaccine against malaria comes just months after a study by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine suggested rising worldwide temperatures could cause a dramatic increase in malaria cases.[8]

According to a report in The Lancet Planetary Health, the European study estimates 8.4 billion people could be at risk from malaria and dengue fever by the end of the century if rising temperatures were to go unchecked and the world’s population continues to ramp up.[9]
While the year 2100 seems a long way off, the European researchers base their dire predictions on “worst-case scenario” effects of greenhouse gas emissions and population density producing warming temperatures of 3.7 degrees Celsius—about 6.6 degrees Fahrenheit.[10]
Malaria could “gradually increase as a consequence of a warming climate in most tropical regions, especially highland areas,” said the report, citing countries potentially at risk as including Ethiopia, Kenya, South Africa, Somalia, Saudi Arabia, Peru, Mexico and Venezuela.[11]
What’s more, researchers also predict changes to weather patterns could cause a “northward shift” of the malaria-epidemic belt into North America, northern and central Europe and northern Asia if temperatures heat up, placing populations in the developed and largely malaria-free nations of the West at risk.[12]
But researchers also acknowledge their study faces limitations because they’re unable to predict advances in vaccines and drugs, or future mutations in malaria parasites.[13]
Malaria ‘Cat and Mouse’
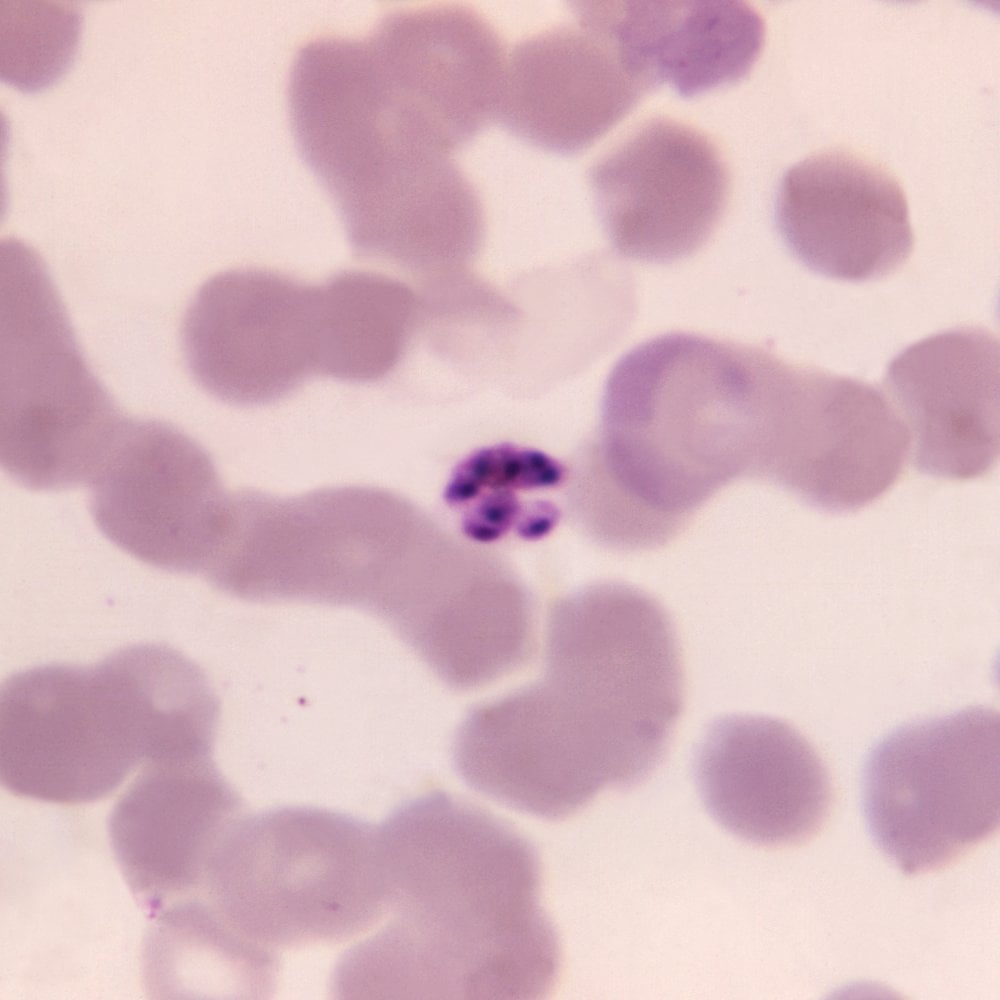
Meanwhile, researchers at Texas Biomedical Research Institute are playing a game of “cat and mouse” with malaria parasites—trying to catch parasites in the act of mutating into different strains.[14]
Scientists at the San Antonio facility have been studying five different malaria parasite species that infect people, probing how certain parasites mutate as they hide in the liver, where they can lie dormant for months—only to strike later with a vengeance.[15] While such studies of new mutations are in the early stages, it’s hoped they’ll eventually help researchers understand how malaria parasites develop resistance to drugs and evade the body’s immune system. It could also pave the way for new malaria treatments in the future.[16]
What can we do about mosquito-driven scourges? »
One simple way to fight mosquito-borne diseases like malaria, is to consider giving a needy family a simple Mosquito Net. For only $10, Gospel for Asia’s field partners can distribute one of these effective nets to an at-risk family in Asia and provide them with safety from insects during the day and at night.
About GFA World
Gospel for Asia (GFA World) is a leading faith-based global mission agency, helping national workers bring vital assistance and spiritual hope to millions across the world, especially in Asia and Africa, and sharing the love of God. In a typical year, this includes thousands of community development projects that benefit downtrodden families and their children, free medical camps conducted in more than 1,200 villages and remote communities, over 4,800 clean water wells drilled, over 12,000 water filters installed, income-generating Christmas gifts for more than 260,000 needy families, and teaching to provide hope and encouragement in 110 languages in 14 nations through radio ministry. GFA World has launched programs in Africa, starting with compassion projects in Rwanda. For all the latest news, visit the Press Room at https://gfanews.org/news.
Read the rest of this GFA World Special Report: Malaria – It’s Time to Buzz Off! New Vaccine Heralds a Game-Changing Development — Part 2
Read more blogs on Christmas Gift Catalog, Malaria, Mosquito Net and GFA World Special Reports on Patheos from Gospel for Asia.
Learn more about how generosity can change lives. Through GFA World (Gospel for Asia) and its Christmas Gift Catalog, gifts like pigs, bicycles and sewing machines break the cycle of poverty and show Christ’s love to impoverished families in Asia. One gift can have a far-reaching impact, touching families and rippling out to transform entire communities.
Learn more how to save families from the sickening agony or death from malaria through the gift of Mosquito Nets that offer protection from the sting of an infected mosquito and help to give their owner a restful nights sleep.
Learn more about Gospel for Asia: Facebook | YouTube | Instagram | LinkedIn | SourceWatch | Integrity | Lawsuit Update | 5 Distinctives | 6 Remarkable Facts | 10 Milestones | Media Room | Water Scarcity | Endorsements | 40th Anniversary | Lawsuit Response | International Offices | Missionary and Child Sponsorship | Transforming Communities through God’s Love
Notable News about Gospel for Asia: FoxNews, ChristianPost, NYPost, MissionsBox
Read what 27 Christian Leaders are affirming about Gospel for Asia.
This Special Report originally appeared on gfa.org.



















