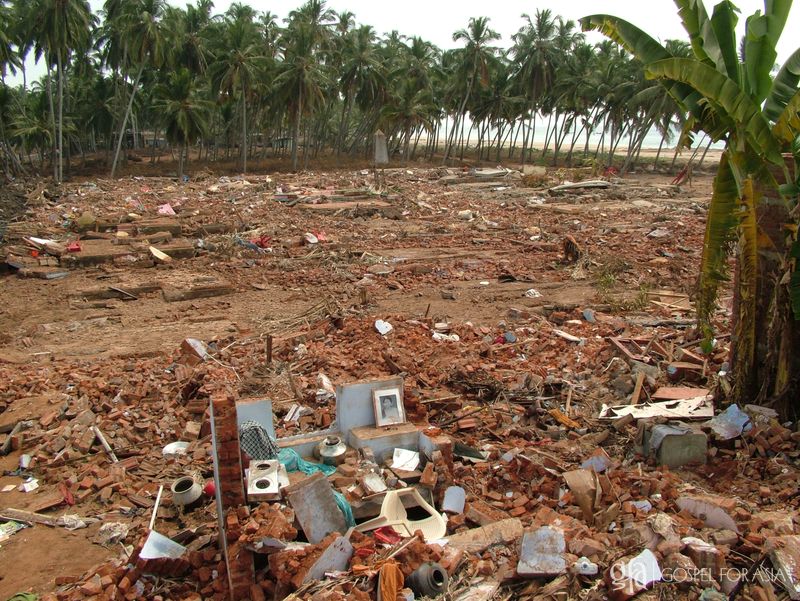
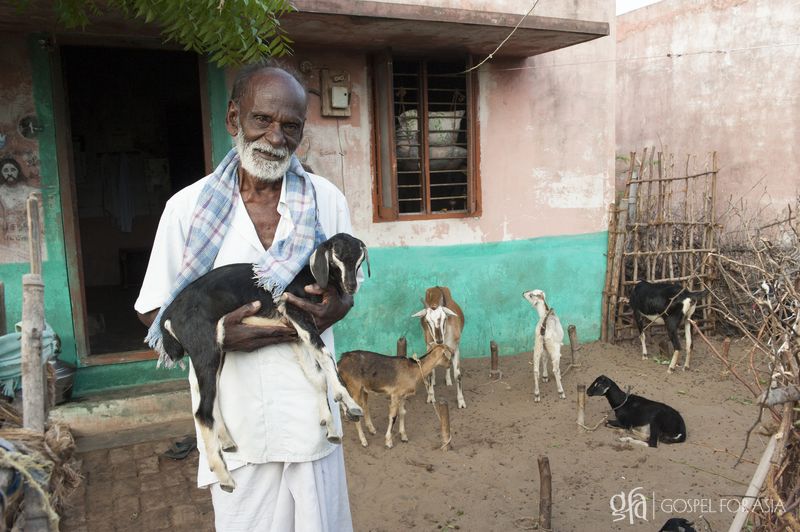
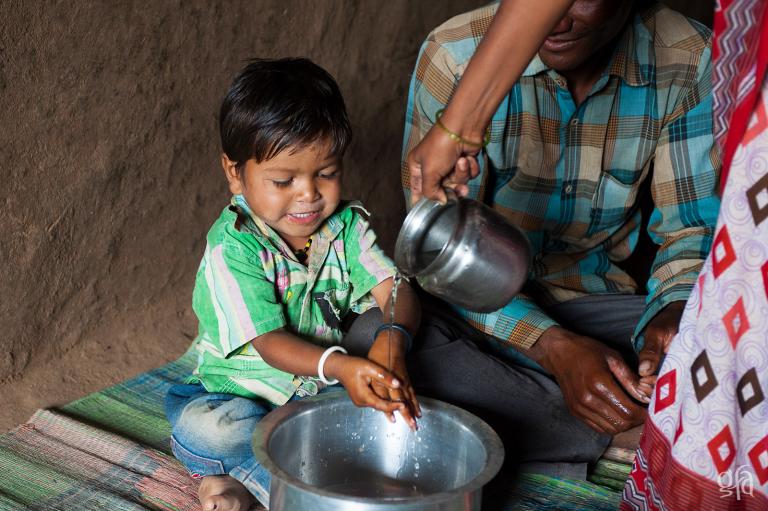
Gospel for Asia (GFA), Wills Point, Texas, Special Report 3/4
So let us take a deep breath. Let us think a moment about that peaceful and stunning NASA photo: AS17-148-22727.

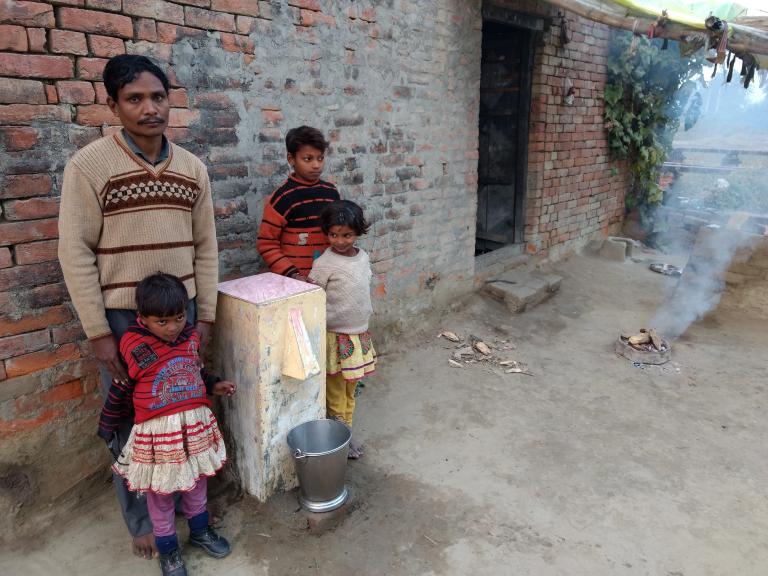
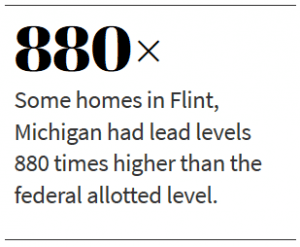
Let us remind ourselves that of all the spinning planets in our solar system, it alone has been created uniquely to sustain water, and that not one other drop has been discovered anywhere else in interstellar space. Let us remember that 75 percent of our planet is covered with water, some 96.5 percent of that in its oceans. Then let us say a prayer for its water resource preservation and purification, and let us remember that some religious systems view water to be holy. Only then, let us absorb the fact that an investigative report by Reuters released December 19, 2016, found nearly 3,000 areas in the United States with lead poisoning rates at least double those in Flint.
This headline tagged a report released by the Associated General Contractors (AGC): “Both Public and Private Studies Find Astounding Gaps Between Current Spending and Projected Needs.” The analysis determined: “Modernizing and replacing aging water infrastructure may be the single largest public works endeavor in our nation’s history. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Clean Water and Drinking Water Infrastructure Gap analysis found a $540 billion gap between current spending and projected needs for water and wastewater infrastructure (combined) over 20 years. Other public studies conducted by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) and the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), and a private study produced by AGC partner, the Water Infrastructure Network, have similarly estimated the nation’s water infrastructure needs to range between $400 and $600 billion over a 20-year period.
The 2014–2017 Flint, Michigan lead-poisoned water crisis highlights possible impacts on communities if warnings are ignored and if appropriate budget planning is not prioritized. (“What is happening to us in Cape Town may not be an outlier. It could happen to you too.”) We need to understand that water degradation and evaporation and infrastructure decline is happening to us now.

So what is the status of clean water worldwide? According to the World Health Organization, some of the global facts regarding safe water usage are these:
71%
of the global population in 2015 (5.2 billion people) used a safely managed drinking-water service—that is, one located on premises, available when needed, and free from contamination.
89%
of the global population in 2015 (6.5 billion people) used at least a basic service. A basic service is an improved drinking-water source within a round trip of 30 minutes to collect water.
840 million
people lack even a basic drinking-water service, including 159 million people who are dependent on surface water (water from rivers and ponds).
2 billion
people globally use a drinking water source contaminated with feces.
502,000
deaths every year are caused by diseases transmitted by contaminated water such as diarrhea, cholera, dysentery, typhoid and polio.
38%
of health care facilities lack an improved water source in low- and middle-income countries. 19 percent do not have improved sanitation, and 35 percent lack water and soap for hand-washing.
In addition to these above statistics, WHO also notes that “Yet diarrhea is largely preventable, and the deaths of 361,000 children aged under five years could be avoided each year if these risk factors were addressed. Where water is not readily available, people may decide handwashing is not a priority, thereby adding to the likelihood of diarrhea and other diseases.”
Is Anyone Doing Anything?
Certainly, organizations somehow, somewhere, are doing something about this? Right? This is the natural response of those of us who unthinkingly use clean water to flush our toilets and allow grey water to be piped into the sewer systems of our communities.
Actually, that thought many of us have when we read about water-distressed systems worldwide is right. Well-meaning help of all kinds, from missionary groups to hundreds if not thousands of non-government organizations to the World Bank and the United Nations to the World Health Organization to inter-agency coordinated efforts to private foundations with substantial granting means to individual governments to the largess of western countries—all of them are players in attempting to solve the water problems of the world.

However, even the best laid plans of sophisticated systems often go awry. Evidence of this is the estimated 50,000 wells in Africa dug by well-meaning organizations that now lie broken, abandoned and non-functional; a dismal testament to good intentions gone bad. Really bad. Jamie Skinner of the London-based International Institute for Environment and Development reported at the 2009 World Water Forum, a triennial summit, on the state of wells in Africa. He is a water development specialist with particular emphasis on West Africa. His report on “water points” included some of these disturbing facts:
- The equivalent of up to $360 million USD has been wasted on building borehole wells that break because they are not maintained or repaired.
- Only one third of water points built by NGOs in Senegal’s Kaolack region are working, and 58 percent in northern Ghana are in disrepair.
- Disrepair occurs because NGOs often do not fully consult with local people before beginning a water project to determine what it will cost to clean and maintain the well.
Some naysayers have deemed this come-do-your-thing-and-go approach as “non-government organizational malfeasance.” Skinner gives the example of a badly constructed and poorly maintained shallow well, dug by a charity in Katine sub county in north-east Uganda, that was full of soil and animal feces and was making the local population sick. The African Medical and Research Foundation’s strategy to solve this well deficiency was to set up a local committee responsible to operate and maintain a new borehole with trained hand-pump repairmen available in case of breakdown. “There is no point in an external agency coming in, putting in a drill-hole and then passing it over to the local community if they can’t afford to maintain it over the next 10 or 20 years,” concludes Skinner.
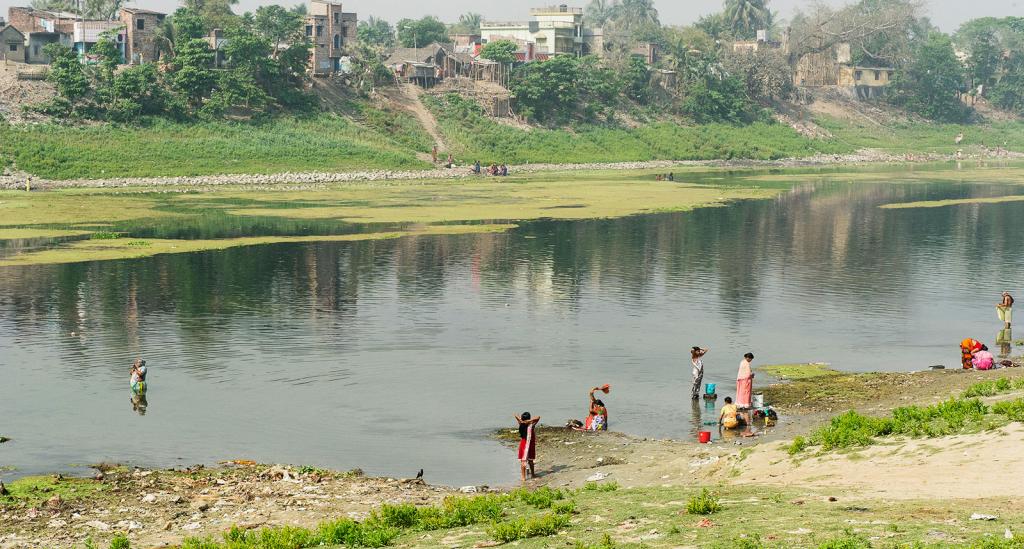

The Need for Clean Water in Asia
In her book Dirty, Sacred Rivers: Confronting South Asia’s Water Crisis, Cheryl Colopy takes us on nearly every footstep of her arduous investigation starting in the headwaters high in the Himalayas.
“This book chronicles my travels in Nepal, India, and Bangladesh, countries that are knit together by the Ganga and her various tributaries. I explain what I learned about glaciers melting in the mountains, sewage gluts and water shortages in the vast cities, and plans for engineering rivers that will have unknown consequences and perhaps limited benefits,” she writes in her introduction.
Interviewing hundreds of Asian water conservation experts who are concerned about their countries’ water shortages and misuse, we have a chance to listen over her shoulder to their love for their land and their attempts to solve water distress issues. Clean water, indeed, is the goal, but working through past mistakes, the consequences of climate change and its unknown future, population explosions, and unintended engineering mishaps gives the reader an extraordinary feeling of being party to all the discussions. As the flap copy explains, “Many are reviving ingenious methods of water management that thrived for centuries in South Asia and may point the way to water sustainability and healthy rivers.”
Simple is often best. Ancient civilizations solved their water needs in ways that speak to us today.
Here too, as with Jamie Skinner’s reporting on Africa’s abandoned wells, a theme emerges, one the author confesses she discovered during her essentially seven-year journey. “There is no way that I—a former medieval scholar turned environment reporter rather later in life—can claim to have answers to South Asia’s water crisis, if there are right answers. So I give you many highly intelligent, trained, sane, and committed water experts from that region. These authorities more often argue for the lighter hand, the softer path; not no engineering at all, but less invasive engineering, and techniques that are localized, decentralized, and draw on traditional methods along with the almost-lost wisdom of local people.”

The themes of the book are: Simple is often best. Ancient civilizations solved their water needs in ways that speak to us today. The people who are most affected by water stresses are most often the ones who can solve the problem.
Indeed, the problems are real.
Sewage in the rivers: “Estimates of the amount of untreated raw sewage that enters the Ganga every day are hard to grasp: apparently something in the neighborhood of a billion liters. Much of it comes from homes that do have toilets, where relatively clean water is being flushed away and turned into sewage, which then turns rivers into sewers, a further loss of clean water.”
Climate change: “This lack of snowfall is the chief problem Dobhal (a glacier specialist) has seen in the high mountains in recent years. As a consequence, the glaciers are depleting, not developing. With good winter snowfall, they stay in balance, and the melting rate is not cause for alarm. Melting glacier ice accounts for 30 percent of the water in the rivers. The rest is from snow and from the monsoon. Now that there is less snow, the spring flow in the rivers comes directly from the older ice. When glaciers lose their volume, the rate of melting increases. It’s the difference between a melting block of ice and a melting ice cube. Big glaciers create their own climate. They make cold weather. Big glaciers can be more powerful than the sunlight that reaches them. But as glaciers shrink, the power of the sun to melt them grows.” Unpredictable behavior is ahead from flooding due to increased glacier melt to drought to drying rivers. One expert sums up the uncertainty, saying, “Climate change will manifest itself through water. It will affect every sector of life through precipitation, snow, rain, whatever. Livestock, forestry, soil, sanitation, disease, everything. But we have no idea how it’s going to happen.”

Agricultural water scarcity: The global water scarcity problem is not limited to providing potable drinking water for humans, although without it we would not exist. Water is necessary for agriculture, for both crops and animal husbandry.
In water-starved South Africa, the first restrictions on water usage were levied upon the agricultural sector. Now, farmers are renegotiating their leases because they cannot produce enough income. Current economic forecasts anticipate that within the next five years as many as 98 percent of farms will have a negative Net Farm Income.
China’s Ministry of Water Resources recently declared a need “to fight for every drop of water or die.” Twelve northern Chinese provinces suffer from water scarcity. In eight, the scarcity is considered acute. This is particularly significant because those provinces provide 38 percent of the country’s agriculture. The rapid economic expansion in China has placed so much demand on water supplies that 28,000 rivers have disappeared over the past 25 years. The flow of the Yellow River has dwindled to a tenth of what it was prior to 1950. Pollution is so rampant in China that almost 10 percent of the groundwater is not even fit for agricultural use.
These countries and others are in a catch-22. Water for agriculture is limited, but it is needed to grow the crops and animals required to feed the demands of growing populations.
The rapid economic expansion in China has placed so much demand on water supplies that 28,000 rivers have disappeared over the past 25 years.
Recognizing the importance of water conservation, the Kerala Water Authority (KWA) in India is making a concerted effort to bring dramatic reform in their own jurisdiction. Infrastructure can cause as much as 45 percent water loss, far above the national average of 15 percent systemic water loss. As the KWA brings improvements to its clean water delivery system, the potential for positive impact is significant.
On the national level, Indian Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi began promoting the implementation of a decades-old clean water initiative in 2014. One part of that project alone, linking the Ken and Betwa rivers, would make drinking water available for 1.35 million people plus provide enough to irrigate 600,000 hectares of farmable land. The project is pending approval from the environmental ministry, but nonetheless, we’re hopeful of the efforts making strides to resolve India’s water crisis.
In 2016, 330 million Indians were affected by drought, and the government is taking action to respond. “We are working on a big scheme to bring water to farmlands. We need to have a permanent solution to the drought,” the Prime Minister said.
There is a plan underway for 25,000 villages to get clean water wells, and 5,000 wells have been started, as of April 2017.
Dr. KP Yohannan, founder of Gospel for Asia and Metropolitan of Believers Eastern Church, met with high officials in the government in March 2016 to discuss ways in which India’s Christian community could collaborate with the government for the good of the nation. Believers Eastern Church has since been able to work together with the Indian government to work on cleaning up some of the nation’s rivers.
One of those voices Colopy interviewed—a highly intelligent, trained and committed expert—Sudhil Chaudhary, a professor of biology at Bhagalpur University has a plan. His is for forestry restoration, which also involves water reclamation. Sudhil would like local communities to be part of each and every decision about the plan. This is a theme that seems to be emerging all over the world. I find it stated more and more as I research world development needs and particularly, the Millennium Development Goals and its companion the Sustainable Development Goals. Things work when there is community buy-in, and often fail when there is none.
This material appeared in Gospel for Asia’s special report “The Global Clean Water Crisis: Finding Solutions to Humanity’s Need for Pure, Safe Water.”
=====
Click here, to read more blogs on Patheos from Gospel for Asia.
Go here to know more about Gospel for Asia: GFA | GFA.org | Facebook | Youtube
For more information about this, click here.